
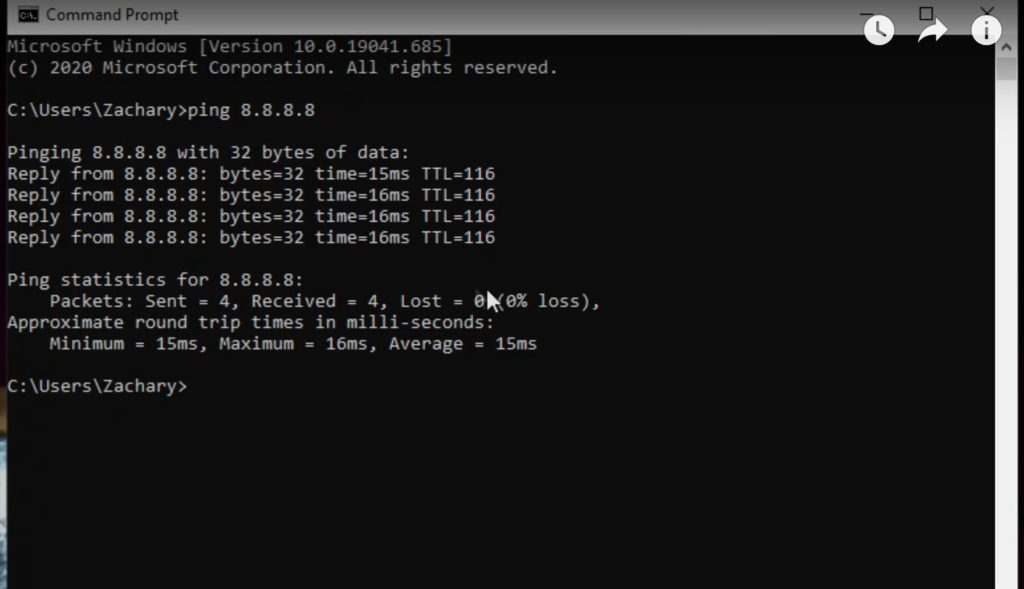
Browsers store the DNS resolution information for frequently-accessed sites. The first step that the browser takes to get the IP address of the computer that hosts is to look in its own storage system. So, given an address such as, the browser focuses on the part, and in fact, initially, just. In order to do this, it only needs to work with the domain name. The browser needs to know the IP address of the host for that Web page before it can go and request the code that builds the page. Once the address of a Web page gets into the address bar of a browser, the search for that requested Web page begins. For example, we will look at how a Web browser functions. There are a number of applications that need to initiate a DNS reference call. If the network gives access to the internet, the system’s users will also get access to a DNS server for internet domain names. Networks run their own DNS servers to record the mappings between hostnames and IP addresses within the private domain. The command’s name derives from “name server lookup.” Its purpose is to query the default domain name server and return information on those mappings between domain names and IP addresses. Nslookup is a networking utility that is available at the command line of any computer that has a network card. DNS reconciles between these two addressing standards. The devices that pass data around don’t understand domain names – they deal with IP addresses. Instead, it travels over IP-based networks.

The Web doesn’t have its own transport system. The domain name is a concept of the World Wide Web. This is a service that maps IP addresses to domain names.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
